How COVID-19 Reveals Existing Biases Against The Disability Community
16:08 minutes

 This segment is part of The State of Science, a series featuring science stories from public radio stations across the United States. This story was reported by Christopher Egusa on KALW.
This segment is part of The State of Science, a series featuring science stories from public radio stations across the United States. This story was reported by Christopher Egusa on KALW.
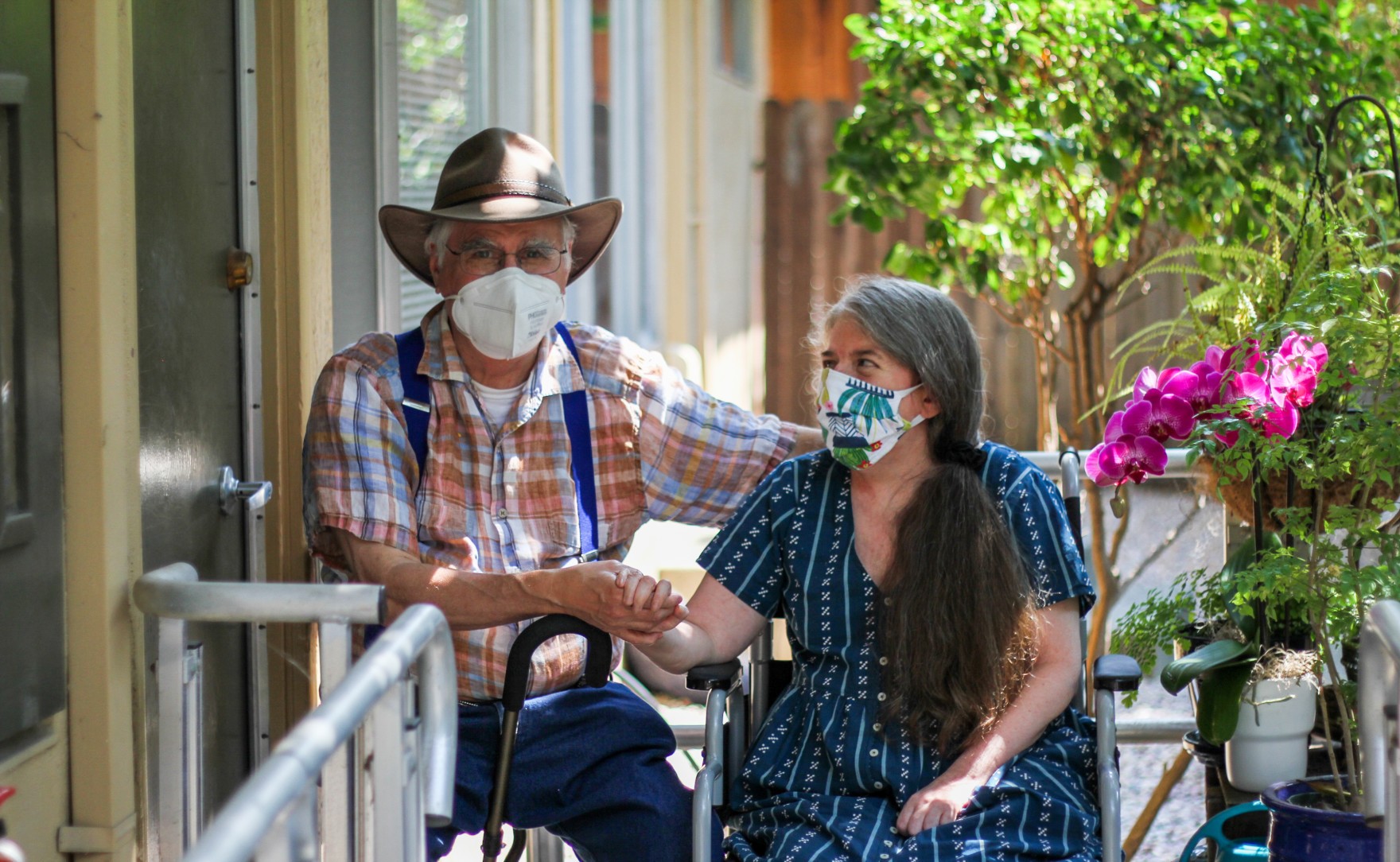
In early July, I visit Ingrid Tischer at the Berkeley apartment she’s shared with her husband, Ken, for the past 10 years. When I arrive, she’s already sitting outside at the top of a gently sloping ramp that leads up to the door.
We’re both vaccinated, but we’re still taking precautions: masks, outdoors, and social distancing. That’s because Ingrid has a severe disability.
“I have muscular dystrophy,” she tells me, “which is a neuromuscular disorder that I’ve had my entire life because it’s genetic.”
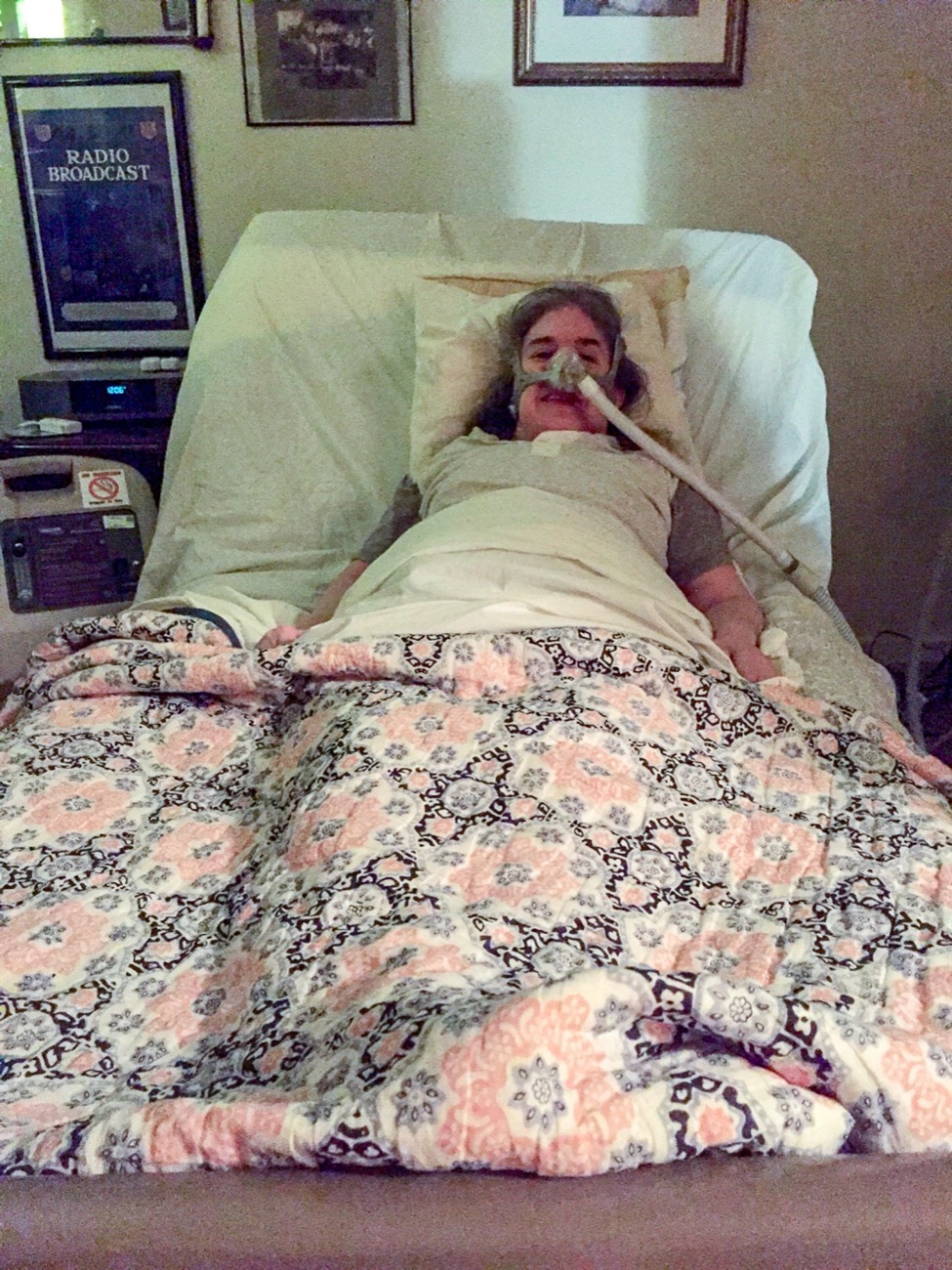
Muscular dystrophy is a progressive muscle wasting disease. It impacts her mobility, including her ability to walk unassisted. Ingrid says she’s most impacted by having a weak respiratory system and uses an oxygen device called a biPap to help her breathe.
Earlier in the pandemic, her doctor told her that if she got COVID, it would likely be a death sentence. “I’d never heard my situation put in such stark, certain terms,” she says.
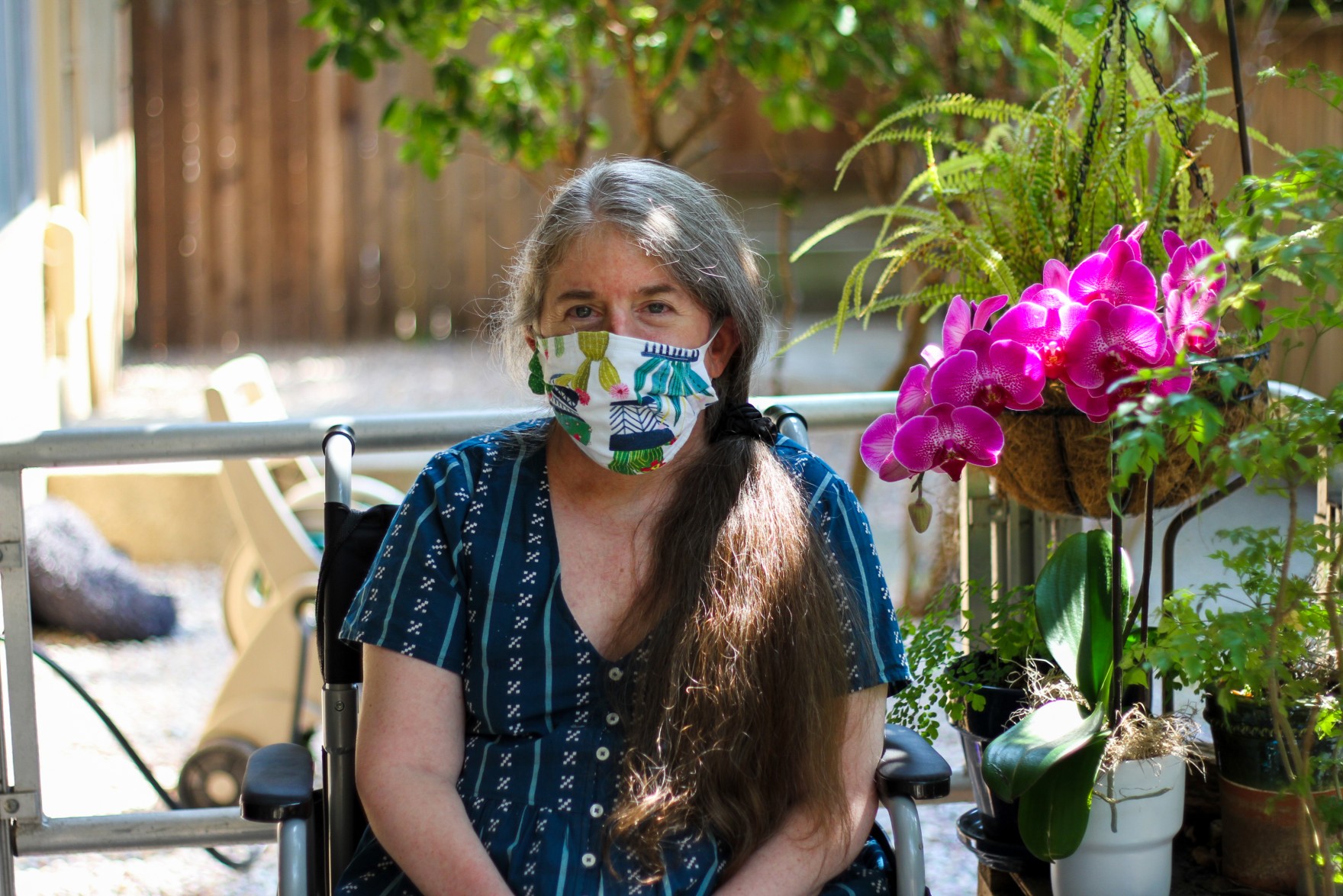

Ingrid is in her mid 50s, with graying brown hair and bright blue eyes. She leads fundraising for DREDF, a disability rights and legal advocacy organization. She’s also a writer — she’s written a draft of a novel and has a blog called “Tales From the Crip.” In addition to a brilliant title, the blog is full of her personal reflections about navigating a world in which the needs and feelings of people with disabilities go mostly unseen and ignored.
When COVID hit in the spring of 2020, Ingrid was terrified. Because of the risk of infection and smoke from the wildfires that summer, she stopped leaving her house entirely, developed severe anxiety and depression, and began noticing a host of new health issues.
Her feet and legs began swelling and breathing became even more difficult than usual. Her doctor worried she might be developing congestive heart failure, but told her to stay home rather than come in for tests and risk infection. It’s a common story. A recent survey by the disability advocacy group #NoBodyIsDisposable found that many disabled people have delayed medical care for over a year due to concerns about COVID-19.
It all came to a head one morning in January of this year when Ingrid fell trying to get to the bathroom. She wasn’t hurt physically, but it left her shaken. She and Ken decided she had to go to the emergency room, the last place she wanted to be.
“We didn’t know if what we were doing was going into a situation where we would never see each other again.” – Ingrid Tischer
For a disabled person, going into a medical setting can feel like going into battle. A recent study published in the journal Health Affairs found that over 80% of physicians believe that people with disabilities have a lower quality of life.
“Nobody’s about to blame doctors and nurses after what they’ve been doing and what they’ve been through over the last year,” says Jessica Lehman, Executive Director of the advocacy group Senior Disability Action. “But, it’s the nuance of thinking that this person’s life is not going to have as much quality, that this person isn’t going to have as much as much joy and experience, and adventure and success, in whatever way all of that is defined as somebody without a disability. And so, when you’re thinking that way, that’s subconsciously going to come into those split second decisions.”
Including decisions about medical care.
Ingrid has received her medical care from Kaiser since the mid 90s. “The providers, the doctors, the nurses, everybody else, for the most part is quite good. And pretty enlightened around disability,” she says.
During the first part of her six day hospital stay, that continued to be true. She was admitted to an acute floor for neurological conditions. There, she was diagnosed with pneumonia, placed on antibiotics and a diuretic for the swelling, and hooked up to a breathing machine. Her physical needs were being met, but her emotional state was still crumbling.
Then she had an experience that completely threw her for a loop.
As her discharge date got closer, Ingrid worried about her life at home after having lost so much function. She’d heard about a special in-patient rehab program that sounded perfect.
There was just one problem: they don’t usually take patients with progressive conditions like Ingrid’s. She asked to talk about it with the neurologist who’d been assigned to her.
“I said it really sounds exclusionary,” she says. “I didn’t say discriminatory, but I said exclusionary.”
She and her husband, Ken, say that the neurologist’s demeanor suddenly changed and his tone got sharper. She was also in an extremely vulnerable state: lying in bed, suffering from pneumonia, wearing an oxygen mask, and still in acute emotional distress.
“It’s all been documented in the chart,” she says. “And he said to me, ‘Well, look,’ and he gestured to my body. And he said, ‘Well, look at you. You’ve always known this was coming.’”
Ken wrote the exchange down directly after the experience. He says the neurologist continued, “‘This has been coming for a long time. And you know, there’s nothing we can really do about it.’ That was in quotes.”
Ingrid says she felt like she’d been punched in the gut. And, she interpreted what he said even more darkly.
“He, I thought, was saying, ‘Look, you’re like, you’re past the point of no return. You know, why do you expect us to do anything? You’re not worth the resources.’ Basically, there’s no point.”
The exchange sent her spiraling. The next night she had a panic attack, which she’d never experienced before.
Ken visited her the next day. “She was shaking when I went in there,” he says. “She was shaking and quivering. And she was sitting up in bed. And she said, ‘Ken, I want you to promise me one thing.’ And I said, ‘What?’ And she said, ‘that I can come home to die. You’ll have me at home to die.’”
She believed she was at the end of the road.
“So this, if you’ll excuse the expression,” Ingrid says, “this guy’s f***ed with my head at a moment when I was extremely vulnerable, even though he probably didn’t mean to. I could believe that. But he’s a neurologist. He’s gotta know.”
She was successfully discharged and, with the proper support and exercise regimen, Ken says her condition has completely turned around. “Oh, 180 degrees,” he says. “He didn’t know what he was talking about.”
Many studies have shown that doctors tend to be overconfident in their own diagnostic abilities.
And Ingrid says this experience is far too familiar.
“This was, by far, not even close to the only time I’ve had an encounter like this with a medical doctor.”
The difference, she says, is that this time she was in the midst of a psychiatric emergency.
Nearly every disabled person I’ve talked with has their own stories of pain and discrimination. The dismissal and invisibility are common experiences.
“I think in the COVID pandemic we saw the most horrible manifestation of ableism and ageism that I’ve ever seen.” – Jessica Lehman
Jessica Lehman explains that this same bias was playing out across a series of battlegrounds throughout the pandemic.
“I think in the COVID pandemic we saw the most horrible manifestation of ableism and ageism that I’ve ever seen,” she says.
The first of these battlegrounds was the state’s Crisis Standards of Care, a document directing hospitals and doctors on how to ration scarce medical care. It attempts to answer the question: who gets treatment and who doesn’t?
You may have heard about medical care rationing early in the pandemic, from countries like Italy. As medical supplies ran low, doctors were faced with excruciating choices about who to put on lifesaving treatment.
Across the U.S., ICU beds and ventilators started running low, prompting many states, including California, to review their emergency plans and update their Crisis Standards of Care.
California’s guidelines left the door open for elderly and disabled people to be denied care in favor of someone younger or able-bodied. It sent alarm bells through the disability community, and beyond.
Jessica Lehman also lives with a neuromuscular condition. “I remember thinking, ‘Oh, my goodness, so I could get COVID and I could go to the hospital,’” she says. “And they might say, ‘We don’t have enough ICU beds or ventilators and because you have a disability, you don’t get one.’ And that would be a death sentence.”
“It was like seeing everything that I was aware of—the general societal perceptions and prejudices—seeing it in writing and seeing it legitimized and sanctioned.” – Jessica Lehman
People in the disability community shared news reports from Oregon and other states where a few doctors denied care to people with disabilities. In California, Santa Clara county began taking inventory of ventilators people had at home. Many disabled people feared they might have their equipment taken away and redistributed.
“It was like seeing everything that I was aware of — the general societal perceptions and prejudices — seeing it in writing and seeing it legitimized and sanctioned,” Jessica says. “It was just like, ‘Oh my gosh, I don’t know when we have faced a threat like this. And what are we going to do?’”
The disability community jumped into action. Within a few weeks, 30 organizations had formed the California Care Rationing Coalition.
And it wasn’t just disabled folks. Brandie Sendziak is an attorney with the Independent Living Resource Center San Francisco and cofounder of the online movement #NoBodyIsDisposable.
“It was, you know, the higher weight community, the disabled community, the aging community, all working together from the beginning,” she says. “And, and I really think it helped make a big difference that probably wouldn’t have happened if only one of the communities had stepped up.”
It was kind of like the avengers of advocacy — they had policy groups, legal advocates, and community organizers all working on this one issue: trying to convince the state to revise this document. And the surprising thing is it actually worked.
After many rounds of negotiation and numerous revisions, California’s new Crisis Standards of Care now include an entire section that outlines what factors cannot be used to determine healthcare decisions, including disability.
And because of this intersectional coalition they’d developed, they were prepared for the next battleground.
It didn’t take long. In late 2020, Gov. Gavin Newsom announced plans for the state to begin distributing the vaccine based on a tiered priority list.
Ingrid figured she’d be among the first eligible for the vaccine. She reached out to her doctor, but was told the system wouldn’t let him schedule her. She didn’t qualify, despite her extreme risk. She says she felt invisible and silenced.
She says it was, “the old feeling of like, I’m screaming on a public street and nobody’s noticing. I have, like, a really fragile, super fragile, respiratory system.”
So why wasn’t she being contacted for a vaccine? From the outset of the vaccine rollout, disabled people were placed behind front line workers, caregivers, teachers, older adults, and many others. Jessica Lehman participated in public meetings of the state-run California Vaccine Advisory Committee.
She remembers one slide in a presentation that state officials had put together, which brought everything into stark relief.
“It actually laid out like, what is the goal?” she recalls. “And on the one side, it said, if the goal is reducing fatalities, then we need to vaccinate seniors and people with disabilities because those are the groups more likely to die, right? Or, if the goal is getting the economy functioning again, then we vaccinate workers so that they can go back to work and open stores and restaurants again.”
She says it was like the two groups were pitted against each other.
“It just brought to my head everything about seniors and people with disabilities being seen as a drain on society.”
Then, in January 2021 Governor Newsom made an announcement that shocked the disabled community: vaccines would be distributed by age only. Disabled folks would have to wait to get vaccinated with the general public.
Once again, the “disability advocacy avengers” fought back. And once again, the state relented, opening up vaccination for people with certain disabilities and chronic conditions in mid-March.
But, as with many wins for this community, the victory felt incomplete. The list of qualifying conditions was limited. Most people with disabilities would need to get approval from their doctor.
Jessica says that’s inherently inequitable.
“We know that white people and people with money are far more likely to have a doctor who they trust and who trusts them and to have access to medical care to be able to make that happen,” she says. “And so this felt like a moment where it wasn’t okay to celebrate that. Like, if it’s not all of us, then it’s none of us.”
Now, most people who want to get vaccinated are able to. But, the spread of the delta variant is bringing up equity issues again. Hospitals in low-vaccination states like Idaho, Alabama, and Texas are talking care rationing again.
In California, advocates are staying vigilant, holding the state to the less-biased guidelines. Jessica, however, still has doubts. “Do hospitals follow them? It’s not really binding and it’s really hard to know,” she says.
“After 55 years of disability, I don’t think I’ve ever felt more profoundly let down by the health care system.” – Ingrid Tischer
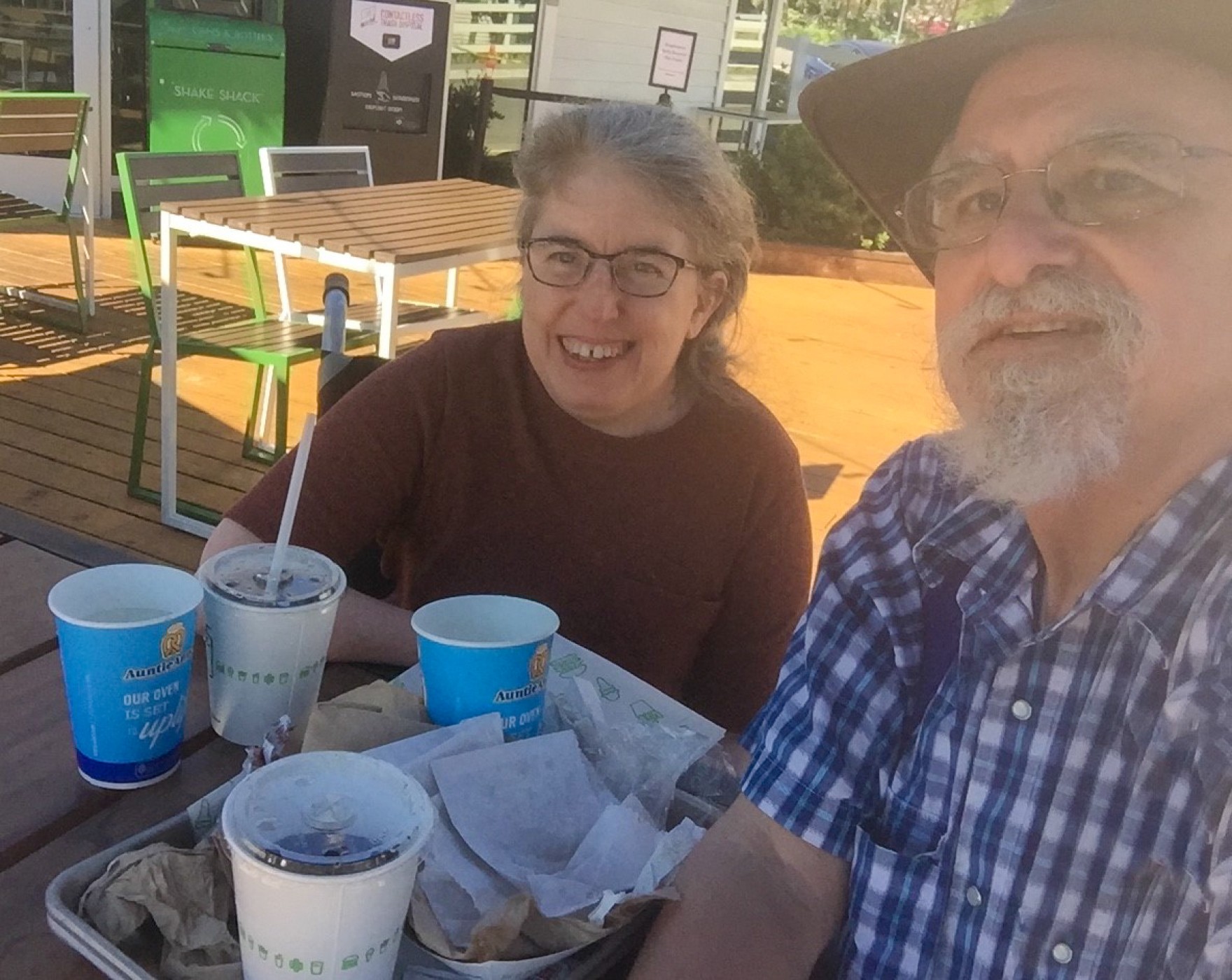

For Ingrid, the last 18 months have left her with little faith. “After 55 years of disability, I don’t think I’ve ever felt more profoundly let down by the health care system,” she says.
She’s once again been left off the list for the CDC-recommended booster vaccine for at-risk people and that feels like deja vu.
But despite the new fears, she’s been improving both physically and mentally. She and her husband went out for the first time in July. They got burgers and sat outside. And she’s back to working remotely at the disability rights organization — once again fighting for equity. And for the right of disabled folks to be seen, acknowledged, and valued.
Christopher Egusa reported this series while participating in the USC Annenberg Center for Health Journalism‘s 2021 California Fellowship.
Audio Piece Credits
Engineering: James Rowlands
Editing: Lisa Morehouse
Editing Assistance: Abukar Adan
Invest in quality science journalism by making a donation to Science Friday.
Ingrid Tischer is Director of Development at the Disability Rights Education and Defense Fund (DREDF) in Berkeley, California.
Ken Stein is retired in Berkeley, California.
Jessica Lehman is Executive Director of Senior Disability Action in San Francisco, California.
Brandie Sendziak is a staff attorney at the Independent Living Resource Center of San Francisco in San Francisco, California.
IRA FLATOW: This is Science Friday. I’m Ira Flatow, and now, it’s time to check in on the state of science.
SPEAKER 1: This is KERE–
SPEAKER 2: For WWNO–
SPEAKER 3: St. Louis Public Radio–
SPEAKER 4: KKBB New–
SPEAKER 5: Iowa Public Radio News.
IRA FLATOW: Local science stories of national significance. We’ve been following the stories of how the COVID 19 pandemic has overburdened hospitals and impacted care for those suffering from non-COVID related illnesses. We’ve also seen how these last few years have shown many of the cracks in our health care system and revealed longstanding disparities.
Reporter Chris Egusa has been examining the impact on the disabled community in California for station KALW in San Francisco. He introduces us to a woman who recounts her harrowing experience in the hospital as a disabled person. And we’ll meet the disability advocates fighting the bias they found infused throughout the state’s pandemic response. Here’s Chris.
KEN TISHER: Hi, Ingrid. Here’s your guys.
CHRIS EGUSA: Oh, hi, Ingrid. Yes.
KEN TISHER: I’m getting them some water and a TV tray.
INGRID TISHER: Oh, very nice.
CHRIS EGUSA: Should I set up right over here?
INGRID TISHER: Wherever you’d like.
CHRIS EGUSA: OK.
Ingrid Tisher has lived in this Berkeley apartment with her husband, Ken, for the past 10 years. When I arrive, she’s already sitting outside at the top of a gently sloping ramp that leads up to the door.
I mean, if you’re OK with it, I think maybe up there would be good for the audio.
INGRID TISHER: Yeah, especially since we’re wearing masks.
CHRIS EGUSA: Yeah, yeah.
We’re both vaccinated, but we’re still taking precautions. Masks, outdoors, social distancing. That’s because Ingrid has a severe disability.
INGRID TISHER: I have muscular dystrophy, which is a neuromuscular disorder that I’ve had my entire life, because it’s genetic.
CHRIS EGUSA: It’s a progressive muscle wasting disease, which impacts her mobility, including her ability to walk unassisted. Her respiratory system is weak, so she uses an oxygen device called a BiPAP to help her breathe. Earlier in the pandemic, her doctor told her that if she got COVID, it would likely be a death sentence.
INGRID TISHER: I’d never heard my situation put in such stark, certain terms.
CHRIS EGUSA: Ingrid is in her mid-50s, with graying brown hair and bright blue eyes. She leads fundraising for a disability rights organization, and she’s a writer. When COVID hit in the spring of 2020, Ingrid was terrified. Because of the risk of infection, and smoke from the wildfires that summer, she stopped leaving her house entirely. She developed anxiety and depression and a host of new health issues. Her feet and legs began swelling. Breathing became more difficult. Her doctor was worried she might be developing congestive heart failure, but because of the risk, told her to stay home rather than come in for tests.
And that’s not uncommon. A recent survey by a local advocacy group found that many disabled people have delayed medical care for over a year. It all came to a head one morning in January of this year, when Ingrid had a fall trying to get to the bathroom. She wasn’t hurt physically, but it left her shaken. She and Ken decided she had to go to the emergency room, the last place she wanted to be.
INGRID TISHER: We didn’t know if what we were doing was going into a situation where we would never see each other again.
CHRIS EGUSA: When Ingrid entered Kaiser’s emergency room in Oakland–
INGRID TISHER: It was like being wheeled into the lion’s den of the lion’s den.
CHRIS EGUSA: For a disabled person, going into a medical setting can feel like going into battle. A recent study from the journal, Health Affairs, found that over 80% of physicians believe that people with disabilities have a lower quality of life.
JESSICA LEHMAN: Like, nobody’s about to blame doctors and nurses after what they’ve been doing and what they’ve been through over the last year.
CHRIS EGUSA: Jessica Lehman is the Executive Director of the advocacy group Senior Disability Action.
JESSICA LEHMAN: But it’s the nuance of thinking that this person’s life is not going to have as much quality, that this person isn’t going to have as much joy and experience and adventure and success in whatever way all of that is defined as somebody without a disability. And so, when you’re thinking that way, that’s subconsciously going to come into those split second decisions.
CHRIS EGUSA: Decisions about medical care. Now Ingrid says she’s been with Kaiser since the mid-90s, and has found that–
INGRID TISHER: The providers, the doctors, the nurses, everybody else for the most part is quite good, and pretty– at least, recently– pretty enlightened around disability.
CHRIS EGUSA: And for the first part of her six day hospital stay, that was also true. The staff quickly diagnosed her with pneumonia, and began treating her physical needs. But her emotional state was still crumbling. Then, she had an experience that completely threw her for a loop. As her discharge date got closer, Ingrid worried about her life at home after having lost so much function. She’d heard about a special inpatient rehab program that sounded perfect. There was just one problem, they don’t usually take patients with progressive conditions, like Ingrid’s. So she asked to talk about it with the neurologist who’d been assigned to her.
INGRID TISHER: And then, I said, well, it really it sounds exclusionary. I didn’t say discriminatory, but I said, exclusionary.
CHRIS EGUSA: She, and her husband, Ken, say that the neurologist’s demeanor suddenly changed, and his tone got sharper. Keep in mind, at this point, she’s as vulnerable as it gets. Lying in bed, oxygen mask, pneumonia, and still in acute emotional distress.
INGRID TISHER: It’s all been documented in the track. And he said to me, well, look. And he gestured to my body, and he said, you’ve always known this was coming.
KEN TISHER: “This has been coming for a long time. And you know there’s nothing we can really do about it.” That was in quotes.
CHRIS EGUSA: Ingrid says she felt like she’d been punched in the gut, and she interpreted what he said even more darkly.
INGRID TISHER: He– I thought was saying, look, you’re past the point of no return. Why do you expect us to do anything? You’re not worth the resources, basically. There’s no point.
CHRIS EGUSA: The exchange sent her spiraling. The next night she had a panic attack, which she’d never experienced before. Ken says when he visited her,
KEN TISHER: She was shaking when I went in there. This is hard to talk about. She was shaking and quivering, and she was sitting up in bed. And she said, Ken, I want you to promise me one thing. And I said, what? And she said, that I can come home to die. That you’ll have me at home to die.
CHRIS EGUSA: She believed she was at the end of the road.
INGRID TISHER: So this– if you’ll excuse the expression, this guy’s [BLEEP] with my head at a moment when I was extremely vulnerable. Even though, probably didn’t mean to. I could believe that. But, he’s a neurologist. He’s got to know.
CHRIS EGUSA: She was successfully discharged, and with the proper supports and exercise regimen, Ken says her condition has completely turned around.
KEN TISHER: Oh, 180 degrees. He didn’t know what he was talking about. He didn’t know what he was talking about.
CHRIS EGUSA: Many studies have shown that doctors tend to be overconfident in their own diagnostic abilities. And, here’s the thing. Ingrid says that this experience, it’s–
INGRID TISHER: By far, not even close to the only time I’ve had an encounter like this with a medical doctor.
CHRIS EGUSA: It’s just that this time, she was in the midst of a psychiatric emergency. Nearly every disabled person I’ve talked with has their own stories of pain and discrimination. The dismissal, the invisibility, it’s common. Advocate Jessica Lehman explains that this same bias was playing out across a series of battlegrounds throughout the pandemic.
JESSICA LEHMAN: We saw the most horrible manifestation of ableism and ageism that I’ve ever seen.
CHRIS EGUSA: The first of these battlegrounds was the state’s Crisis Standards of Care, a document directing hospitals and doctors on how to ration scarce medical care– who gets treatment, and who doesn’t. You may have heard about medical care rationing early in the pandemic from countries like Italy.
SPEAKER 6: Medical supplies and resources are stretched thin, so doctors in Italy are facing unthinkable choices about who gets access to things like beds and respirators, and who does not.
CHRIS EGUSA: Across the US, ICU beds and ventilators started running low.
SPEAKER 7: –rationed care. The state’s top health officials say, Southern California’s COVID numbers are so extreme they’re urging hospitals to review emergency plans, in case they have to limit not only supplies and therapies, but how many people receive life saving care.
CHRIS EGUSA: California’s guidelines, they left the door open for elderly or disabled people to be denied care in favor of someone younger or able-bodied. It sent alarm bells through the disabled community and beyond. Jessica Lehman, the activist, also lives with a neuromuscular condition.
JESSICA LEHMAN: I remember thinking, oh my goodness, I could get COVID and I could go to the hospital, and they might say, we don’t have enough ICU beds or ventilators, and because you have a disability, you don’t get one. And that would be a death sentence.
CHRIS EGUSA: They shared news reports from Oregon and other states where a few doctors denied care to people with disabilities. Here, Santa Clara County began taking inventory of ventilators people had at home. Many disabled people feared they might have their equipment taken away and redistributed.
JESSICA LEHMAN: It was like seeing everything that I was aware of, the general societal perceptions and prejudices, seeing it in writing, and seeing it legitimized and sanctioned. It was just like, oh my gosh, I don’t know when we have faced a threat like this. And, what are we going to do?
CHRIS EGUSA: What they did was jump into action. Within a few weeks, nearly 30 organizations had formed the California Care Rationing Coalition. And it wasn’t just disabled folks. Brandi Senziak is an attorney and co-founder of the online movement Nobody Is Disposable.
BRANDI SENZIAK: It was the higher weight community, the disabled community, the aging community, all working together from the beginning. And I really think it helped make a big difference that probably wouldn’t have happened if only one of the communities would have stepped up.
CHRIS EGUSA: It was kind of like, the avengers of advocacy. They had policy groups, legal advocates and community organizers all working on this one issue– trying to convince the state to revise this document. And the thing is, it worked. California’s Crisis Standards of Care now include an entire section that outlines what factors cannot be used to determine health care decisions, including disability.
IRA FLATOW: You’re listening to the Special Report about disability and the COVID pandemic. This is Science Friday from WNYC Studios. Reporter Chris Egusa has been following the story of disability advocates in California as they fight against bias in the medical system. Chris tells us that this group worked to change the state’s Crisis Standards of Care to make sure disabled people were not discriminated against during the pandemic.
CHRIS EGUSA: And because of this intersectional coalition they developed, they were prepared for the next battleground. It didn’t take long.
SPEAKER 8: Good evening. We begin tonight with Governor Gain Newsom rolling out a new COVID 19 vaccine distribution plan for the state.
CHRIS EGUSA: Ingrid figured she’d be among the first eligible for the vaccine. She reached out to her doctor, but–
INGRID TISHER: He said the system wouldn’t let him. And he just said, I don’t know what to tell you.
CHRIS EGUSA: She says she felt invisible and silenced.
INGRID TISHER: The whole feeling of like, I’m screaming on a public street, and nobody’s noticing. I have, like, a really fragile, super fragile, respiratory system.
CHRIS EGUSA: So why wasn’t she being contacted for a vaccine? Well, from the outset of the vaccine rollout, people with disabilities and chronic illness were placed behind frontline workers, caregivers, teachers, older adults and many others. Jessica Lehman participated in public meetings of the state run California Vaccine Advisory Committee. She remembers this one slide in a presentation that state officials had put together, which brought everything into stark relief.
JESSICA LEHMAN: It actually laid out what is the goal. And on the one side it said, if the goal is reducing fatalities, then we need to vaccinate seniors and people with disabilities, because those are the groups more likely to die, right. Or, if the goal is getting the economy functioning again, then we vaccinate workers, so that they can go back to work and open stores and restaurants again.
CHRIS EGUSA: It was like the two groups were being pitted against each other.
JESSICA LEHMAN: It just brought to my head everything about seniors and people with disabilities being seen as a drain on society.
CHRIS EGUSA: Then, in January 2021, Governor Newsom made an announcement that shocked the disabled community– vaccines would be distributed by age only. Disabled folks would have to wait to get vaccinated with the general public. Once again, the disability advocacy avengers fought back. And once again, the state relented, opening up vaccination for people with certain disabilities and chronic conditions in mid-March. But, as with many wins for this community, the victory felt incomplete. The list of qualifying conditions was limited. Most people with disabilities would need to get approval from their doctor.
JESSICA LEHMAN: And we know that white people and people with money are far more likely to have a doctor who they trust, and who trusts them, and to have access to medical care to be able to make that happen. And so, this felt like a moment where it wasn’t OK to celebrate that. If it’s not all of us, then it’s none of us.
CHRIS EGUSA: Now, most people who want to get vaccinated, can. But the spread of the Delta variant is resurfacing questions about equity. And hospitals in low vaccination states like Idaho, Alabama, and Texas are talking care rationing again. In California, advocates are staying vigilant, holding the state to the less biased guidelines.
JESSICA LEHMAN: But, do hospitals follow them? It’s not really binding, and it’s really hard to know.
CHRIS EGUSA: For Ingrid, the last 18 months have left her with little faith.
INGRID TISHER: You know, after 55 years of disability, I don’t think I’ve ever felt more profoundly let down by the health care system.
CHRIS EGUSA: She says she’s once again been left off the list for the CDC recommended booster vaccine for at risk people, and that feels like deja vu. But, despite the new fears, she’s been improving, both physically and mentally. She and Ken went out for the first time in July. They got burgers and sat outside. And she’s back to working remotely at the Disability Rights Organization, once again, fighting for equity, for the right of disabled folks to be seen, acknowledged, and valued. For Science Friday, I’m Chris Egusa.
IRA FLATOW: Thank you, Chris. His story originally aired on KALW in San Francisco, and was produced as a project for the USC Annenberg Center for Health Journalism’s 2021 California fellowship. Abukar Adan provided editorial assistance. The engineer was James Rowland.
Copyright © 2021 Science Friday Initiative. All rights reserved. Science Friday transcripts are produced on a tight deadline by 3Play Media. Fidelity to the original aired/published audio or video file might vary, and text might be updated or amended in the future. For the authoritative record of Science Friday’s programming, please visit the original aired/published recording. For terms of use and more information, visit our policies pages at http://www.sciencefriday.com/about/policies/
Christie Taylor was a producer for Science Friday. Her days involved diligent research, too many phone calls for an introvert, and asking scientists if they have any audio of that narwhal heartbeat.
John Dankosky works with the radio team to create our weekly show, and is helping to build our State of Science Reporting Network. He’s also been a long-time guest host on Science Friday. He and his wife have three cats, thousands of bees, and a yoga studio in the sleepy Northwest hills of Connecticut.
Christopher Egusa is a reporter and an Audio Engineering Fellow at KALW Public Radio.
Ira Flatow is the founder and host of Science Friday. His green thumb has revived many an office plant at death’s door.