One For All: A Natural Resources Game
In this game from Population Education, students must use cooperative decision making strategies to manage a renewable resource.
Salad Dressing Science: Emulsion Lab
In this experiment, you will test a few common household ingredients to see which is the most effective emulsifier for making salad dressing – and you can eat your results!
Balloon Rockets
In this lesson from the Chemical Educational Foundation, apply the concepts of pressure and Newton’s laws of motion to build balloon rockets.
Physics Secrets for Hula Hooping
In this activity from Science Buddies, kids will create their own hula hoops and investigate how the hoops’ masses affect how they spin. Which do you think will spin better, a heavy hoop or a lighter one?
Have A Cricket Tell You The Temperature!
Investigate why crickets chirp. Then, using observations and math, learn how these insects can help you determine the temperature!
Chocolate Crystal Concoctions
Act like an experimental chocolatier and determine how different melting and cooling procedures impact the shine, hardness, and texture of finished chocolate.
Make a Model Eardrum to Detect Sound Waves
Create a model eardrum to visualize sound vibrations, and then use a smartphone to identify your model’s natural frequencies.
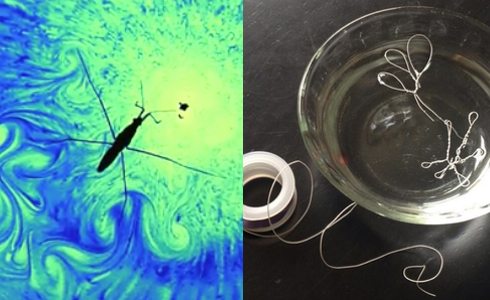
Make A Wire Critter That Can Walk On Water
Learn how insects have inspired engineers and design your own water-walking critter using thin wire and your knowledge of surface tension.
Make a Model of a Home Made From Shipping Containers
Watch an interview with a couple who built a home from shipping containers. Then, design and construct a scale model of a unique shipping container home using printed templates, and estimate the cost of flooring and paint based on model dimensions.
Use Clues to Solve an Ice Mystery
Use the physical characteristics of ice to determine where and how several mystery samples could have been frozen.